Why Multilayer PCBs Are Critical for High-Speed Digital Devices
In the age of rapid technological advancement, high-speed digital devices are becoming increasingly compact, powerful, and complex. From smartphones and laptops to networking equipment and automotive electronics, these systems demand fast data transmission, minimal signal interference, and robust electrical performance. At the heart of these capabilities lies a crucial component: the multilayer printed circuit board (PCB).
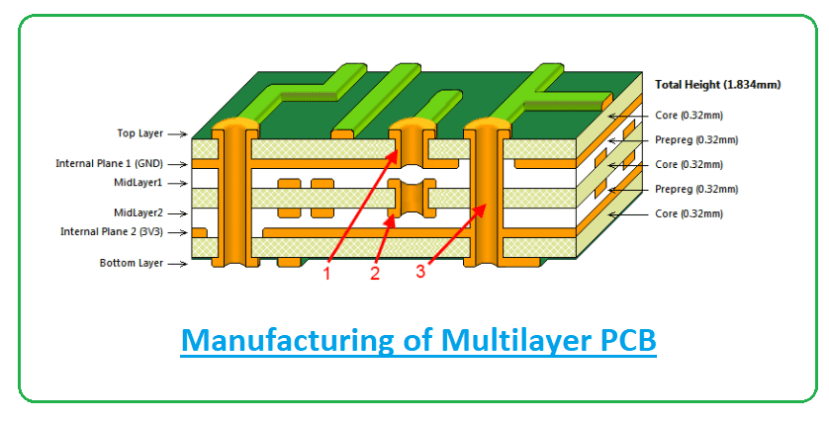
What Are Multilayer PCBs?
A multilayer PCB consists of three or more layers of conductive copper foil separated by insulating materials, all laminated into a single board. Unlike single-layer or double-layer PCBs, which offer limited routing and signal isolation, multilayer boards allow for far more intricate circuit designs by providing multiple planes for power, ground, and signal paths.
Why Multilayer PCBs Matter in High-Speed Digital Devices
1. Enhanced Signal Integrity
High-speed signals are prone to noise, reflections, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Multilayer PCBs help mitigate these issues by:
- Providing dedicated ground and power planes, which reduce noise and allow for better return paths.
- Enabling controlled impedance routing, which is critical for high-frequency signals to travel without distortion.
- Offering shorter signal paths, which reduce delay and signal loss.
2. Higher Density and Compact Design
Modern digital devices require more components in less space. Multilayer PCBs support:
- Denser circuit layouts, allowing more functionality in a smaller footprint.
- The use of surface mount technology (SMT) and via-in-pad designs, which save space and improve performance.
- Compact form factors ideal for smartphones, wearables, and other miniaturized electronics.
3. Improved Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Multilayer designs enhance EMC by:
- Reducing loop areas through closer placement of signal and return paths.
- Shielding sensitive signals using internal layers.
- Ensuring better isolation between high-speed and low-speed signals, reducing cross-talk.
4. Power Distribution Efficiency
With dedicated internal power and ground planes, multilayer PCBs allow for:
- Stable power delivery across complex circuits.
- Reduced voltage drops and noise on power lines.
- Better thermal management, especially when used with heat-dissipating materials or embedded heatsinks.
5. Reliability and Durability
Multilayer PCBs are often manufactured with:
- High-quality materials like FR-4, polyimide, or Rogers laminates, which withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress.
- Advanced lamination processes that improve board strength and reduce the risk of delamination or warping.
- Rigorous testing for signal integrity, layer alignment, and via integrity, ensuring long-term reliability in mission-critical devices.
Applications of Multilayer PCBs in High-Speed Digital Systems
Multilayer PCBs are essential in devices and systems such as:
- Telecommunications equipment: Routers, switches, and servers.
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops.
- Automotive systems: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, and electric vehicle (EV) control units.
- Medical electronics: Diagnostic machines, wearable health monitors, and imaging systems.
- Aerospace and defense: Radar systems, satellites, and avionics.
Final Thoughts
As the demand for faster, smaller, and more reliable electronic devices grows, multilayer PCBs are no longer optional—they’re essential. Their ability to support high-speed signal transmission, maintain signal integrity, and deliver compact, durable designs makes them the backbone of modern digital electronics. Whether you’re developing next-generation communication gear or advanced computing systems, investing in high-quality multilayer PCB design and manufacturing is critical to performance and success.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!