Uses Of ABAP In SAP Environment
Introduction
ABAP is the core programming language used in the SAP environment. SAP uses ABAP to control business logic and system behaviour. Organizations rely on ABAP to customize standard SAP functions. ABAP supports reports, interfaces, enhancements, and automation. It works closely with SAP databases and application servers to deliver secure and reliable enterprise solutions. SAP ABAP Online Course helps learners build strong technical skills for SAP system development.

Uses Of ABAP In SAP Environment
ABAP stands for Advanced Business Application Programming. SAP designed ABAP to build and control business logic inside the SAP environment. Companies use ABAP to customize standard SAP modules. ABAP helps teams match SAP systems with real business needs. It works deeply with SAP databases and application servers. ABAP supports reports, interfaces, enhancements, and data processing. SAP consultants and developers must be skilled in ABAP.
1. Custom Report Development
Developers can create custom reports for business users using ABAP. Standard SAP reports often are unable to meet exact requirements. Here, ABAP allows full control over data selection and output format to the developers. Developers write Open SQL to fetch data from SAP tables. They display results using ALV grids for clarity.

This syntax reads material data from the database. SAP buffering allows ABAP to ensure optimized access. Reports support filters, layouts, user inputs and so on. ABAP reports for daily operations and audits make business operations smoother. One can check the courses by SAP ABAP Online Training for the best skill development.
2. Enhancements and User Exits
ABAP supports system enhancements without changing standard code. SAP provides user exits and enhancement spots. Developers inject custom logic using ABAP. This approach protects the system during upgrades. ABAP handles validations and calculations at runtime.
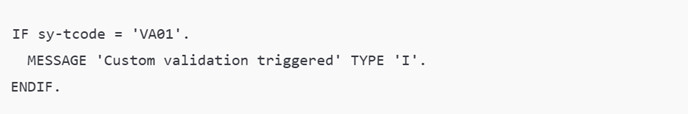
This logic runs during sales order creation. Enhancements allow flexible business rules. Companies use them to enforce policies and controls.
3. Interface and Integration Development
ABAP plays a key role in system integration. External tools like CRM and web apps enable SAP systems to exchange data easily. ABAP supports IDocs, BAPIs, and RFCs. Developers build inbound and outbound interfaces.

This syntax fetches data using a standard API. ABAP ensures secure and consistent data flow. Integration keeps business systems connected. Aspiring professionals are suggested to join SAP ABAP Training in Delhi for complete guidance in this field.
4. Data Migration and Data Processing
ABAP enables users to move data during SAP implementations. One can upload legacy data with ABAP tools such as BDC and LSMW. ABAP validates data before posting.
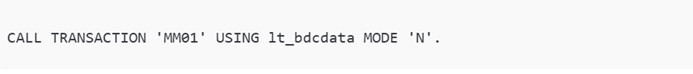
This code creates materials in bulk. ABAP handles large volumes with accuracy. Data migration remains a critical SAP activity.
5. Workflow and Automation
ABAP supports SAP workflows and background jobs. Developers can automate approvals and notifications. ABAP triggers events and tasks. It reduces manual effort and delays.

This syntax schedules a background job. Automation improves efficiency and reliability. More and more businesses today rely on ABAP.
6. Performance Optimization
ABAP helps optimize SAP system performance. Developers tune database access and memory usage. They replace nested loops with joins. ABAP provides tools like SQL Trace and Runtime Analysis.

Optimized code reduces load time. Performance tuning keeps systems stable.
7. Security and Authorization Control
ABAP follows a series of security rules inside SAP. It allows developers to check user authorizations using ABAP statements and protect sensitive data from leaking.

This code checks display permission. ABAP ensures compliance and data safety.
Conclusion
ABAP remains essential in the SAP environment. SAP ABAP Certification Course validates ABAP expertise and improves career opportunities. It enables customization, integration, automation, and security. ABAP matches with SAP systems to meet various business needs. Businesses get complete control over data and operations. The language facilitates stable and scalable solutions for companies. Thus, learning ABAP opens doors to numerous opportunities for aspiring professionals.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!