Asynchronous Support And Performance Optimization In Django
Introduction
Django has adopted asynchronous programming so that scalable and high-performing programs may be created. With ASGI, developers may develop async views that manage many requests simultaneously, hence reducing response times in highly trafficked environments. Reducing superfluous database searches helps to improve the Django ORM even more. Combining async views, wise ORM use, and Django REST Framework best practices enables to provide quick and dependable APIs for developers. Enrol in a Django Course to master web development with practical, real-world projects. This technique guarantees in production settings better scalability, lower latency, and seamless user experiences.

Asynchronous Support And Performance Optimization In Django
Django has developed into a sophisticated framework facilitating asynchronous programming. Django’s ASGI interface enables developers to create views capable of effectively managing simultaneous requests. In high-concurrency situations, asynchronous views and database interactions lower latency. Performance optimization strategies for the ORM and REST APIs guarantee that the application scales seamlessly without bottlenecks.
1. Understanding Asynchronous Views in Django
Django’s asynchronous perspective makes use of Python’s async and await keywords. Django views the view without preventing other incoming requests. Applications doing I/O-bound operations including reading from sockets or making calls to external APIs absolutely need this behaviour.

The view above goes at the same time. The server does not halt for the API call’s completion. This results in decreased response times and better throughput.
2. ASGI and Django Configuration
Since version 3.0, Django offers native support for ASGI. The asgi.py file is comparable to wsgi.py but enables asynchronous execution. The application has to execute on an ASGI server like Daphne or Uvicorn.

Operating Django on an ASGI server guarantees that async views behave as intended. Async views will execute synchronously and forego concurrency advantages if a synchronous WSGI server is used.
3. Optimizing Django ORM Queries
Though strong, Django ORM can create performance bottlenecks if utilized inappropriately. Lazy evaluation of QuerySets causes several queries to be triggered and increases database load. Utilizing select_related and prefetch_related lowers query counts.
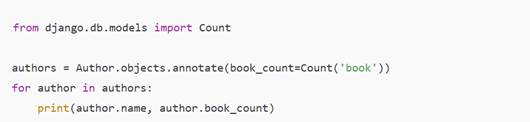
Annotations and subqueries minimize the number of database round trips required.

Performance is also enhanced by accurate indexing on often filtered fields. For more optimization, the EXPLAIN keyword in SQL may be used to examine query plans. Get hands-on experience with expert-led Django Training in Delhi for better career opportunities.
4. Asynchronous ORM Support
Though still experimental, Django is seeing development in native asynchronous ORM support. The aim is to enable database queries to execute free of obstruction of the event loop. Until full support is ready, programmers can use database drivers like tortoises-orm with Django for asynchronous tasks.

This method is great for microservices needing full async I/O.
5. Performance Optimization for Django REST APIs
Async views improve concurrency in Django REST Framework (DRF). Furthermore important are serializer performance. Overuse of SerializerMethodField might cause reaction times to slow down. Efficiency is increased by prefetching related data and lowering serialization depth.

Using Redis to cache often accessed API replies can help to lower database hits. Right pagination also keeps big payloads from slowing the customer and server. Join a beginner-to-advanced Django Course in Noida to build scalable applications with ease.
6. Monitoring and Profiling Django Applications
Profiles aid in spotting slow queries and blocking code pathways. Insights into query execution time and view performance come from tools like django-silk and django-debug-toolbar. Real-time tracking of latency, throughput, and error rates using Prometheus and Grafana is possible.
Conclusion
One great advancement toward creating scalable and responsive applications, asynchronous support in Django helps. Well-structured queries, caching, and pagination help DRF; async views minimize blocking operations; ORM optimizations lower database load. Earn your Django Certification and showcase your expertise to employers worldwide. Running Django on ASGI servers reveals its real concurrency potential. Continuous profiling and monitoring guarantees that under load performance enhancements stay effective.
FAQs
- Why should I study Django?
Development of websites uses Django, a Python framework at the top level. It makes creating scalable, safe programs easier. Django will enable you to quickly develop websites, APIs, and dashboards. Businesses use it often for professional projects.
- How does Django support asynchronous programming?
With ASGI, Django enables async views. This enables the server to simultaneously manage several requests. It increases scalability and response time. For I/O-heavy jobs such API calls or data streaming, async views are beneficial.
- Could Django ORM be tuned for performance?
You can absolutely optimize Django ORM. To prevent N+1 inquiries, employ select_related and prefetch_related. Annotating aggregate data should be done. Find performance bottlenecks by always checking queries with tools such Django Debug Toolbar.
- Does Django suit constructing REST APIs?
Django with Django REST Framework is quite good for APIs. It offers authentication, permissions, and serializers. Fast and safe REST APIs can be built. For apps with high-concurrency, async views make it even better.
- To study Django, do I need previous Python experience?
Indeed, knowledge of fundamental Python is needed. Variables, loops, functions, and classes should all be understood. Django develops on these ideas. Great Python expertise speeds up and simplifies Django learning.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!